The Dorsal-column Medial-lemniscus System Is Particularly Responsive To
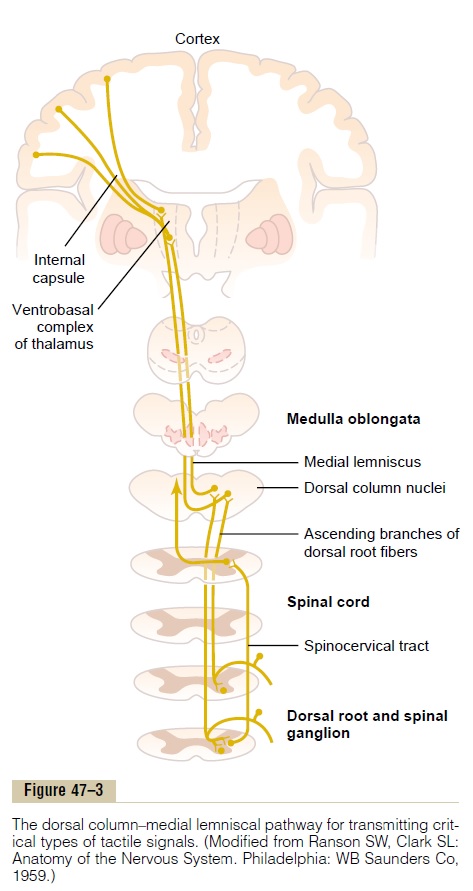
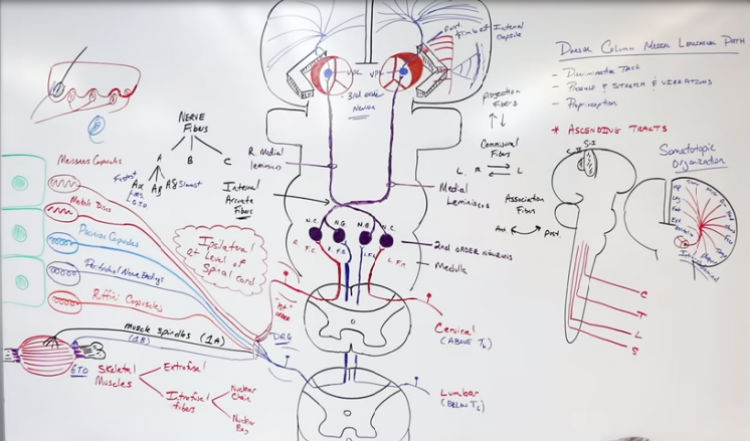
The dorsal-column medial-lemniscus system is particularly responsive to. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors. Medial lemniscus pathway and cuneocerebellar tracts Numerous cutaneous receptors detect and transmit sensory modalities such as light discriminative touch vibration sense proprioception and two-point discrimination. B touch and proprioception.
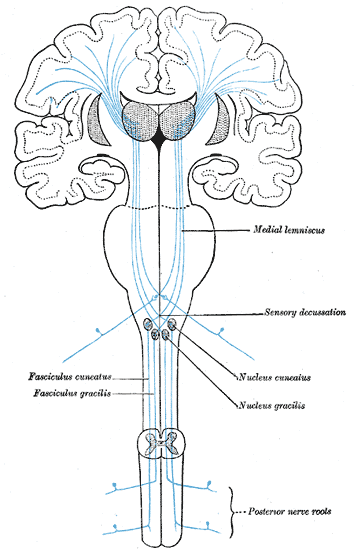
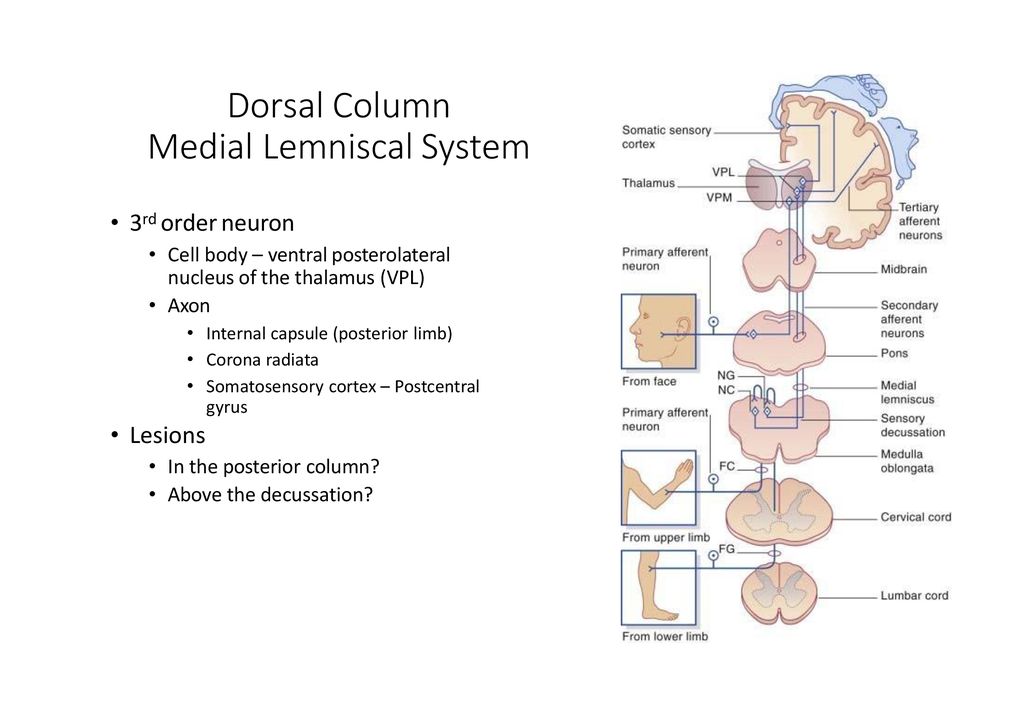
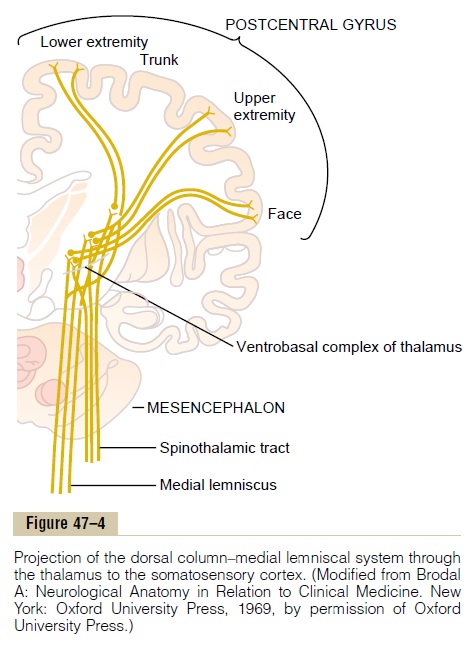
Medial lemnisci in the brain through the medulla pons mid-brain and to the thalamus. Body DRG Term nucleus gracilis or cuneatus 3. The medial lemniscus is part of the larger dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway important for conveying the sensation for fine discriminative touch vibration and conscious proprioception.
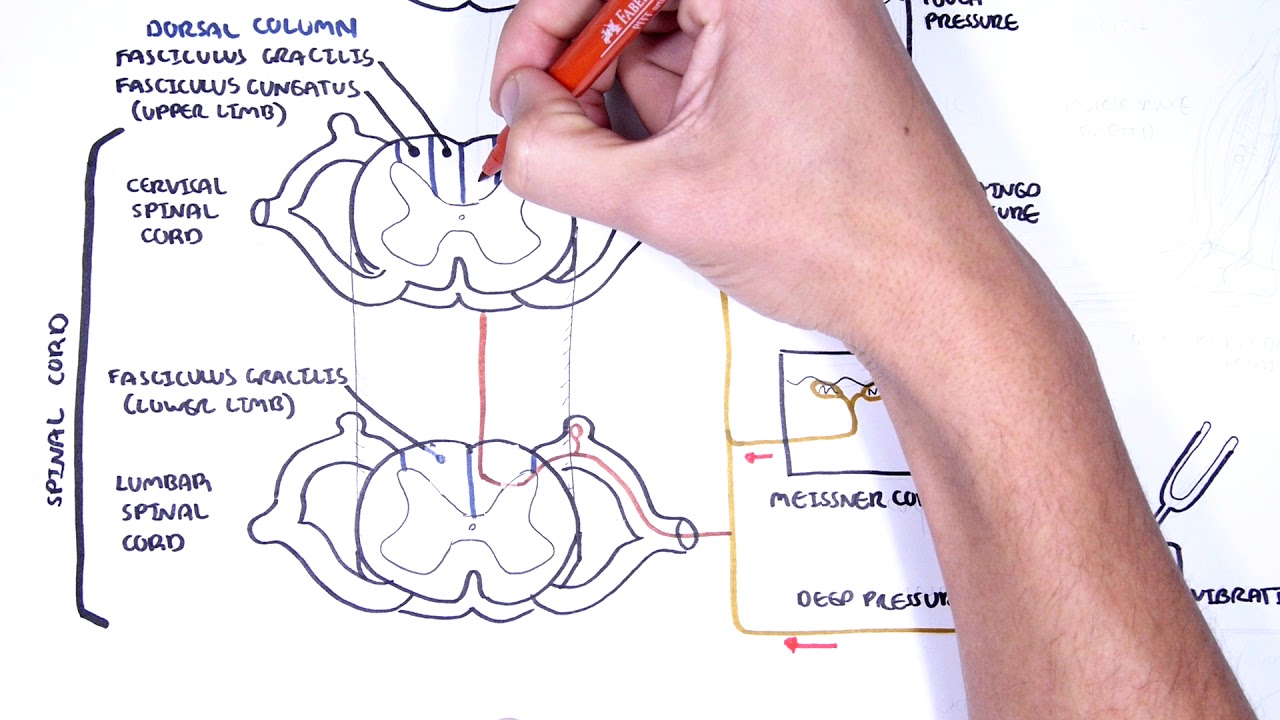
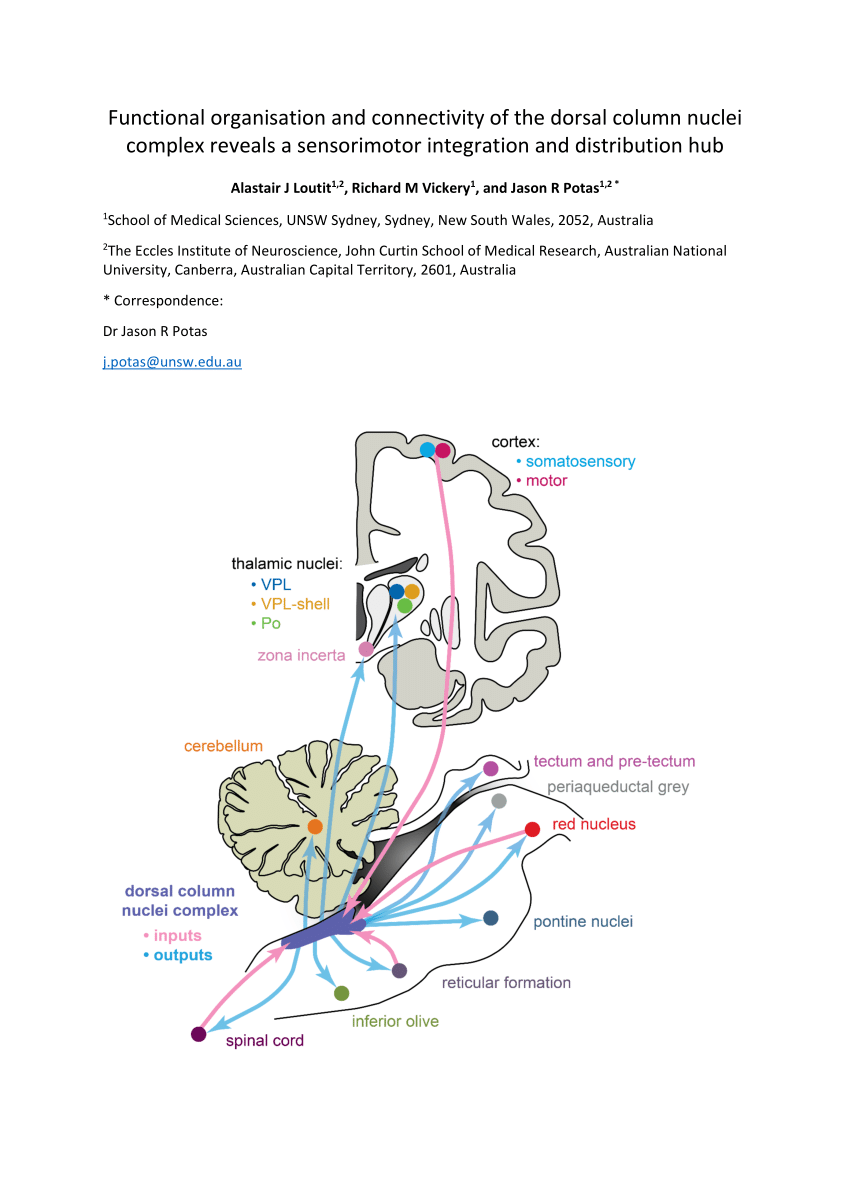
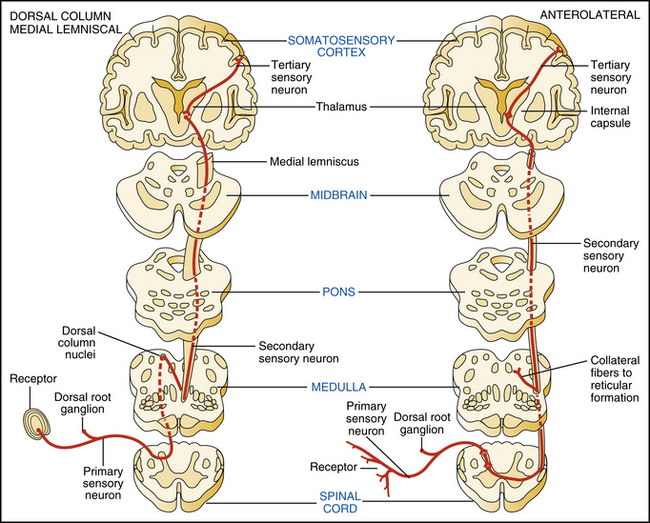
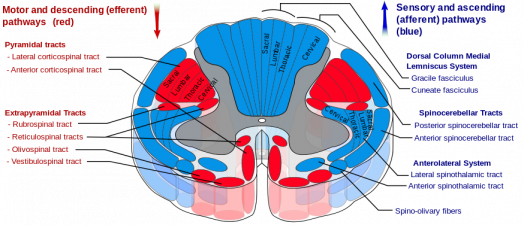
The dorsal column-medial lemniscal pathway DCML carries the sensory modalities of fine touch tactile sensation vibration and proprioception. It conveys sensation of fine touch vibration pressure two-point discrimination and proprioception position from the skin and joints. The is the primary relay nucleus of the somatosensory system for the body receiving input from both the dorsal column-medial lemniscus system and the antero-lateral system.
Also known as the posterior column - medial lemniscus pathway it consists of two. The Medial Lemniscus-Dorsal Column pathway is an ascending spinal tract carrying sensory information to the brain. In the spinal cord information travels via the dorsal posterior columns.
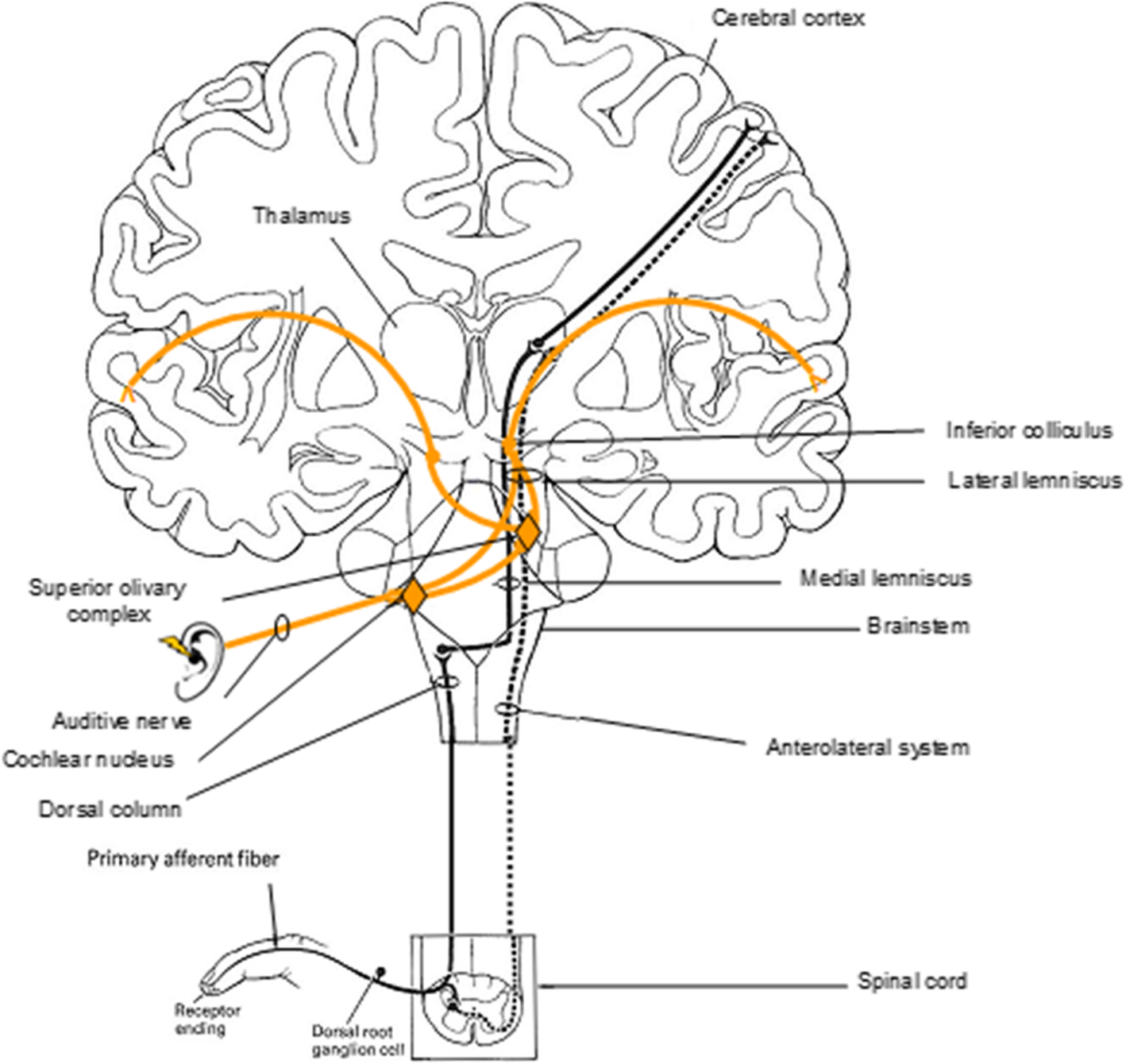
Our skin has several different types of receptors that play a unique role in detecting sensations at our skin free nerve endings Pascinian corpuscles Ruffini endings. In the brainstem it is transmitted through the medial lemniscus. The medial lemniscus also known as Reils band or Reils ribbon is a large ascending bundle of heavily myelinated axons that decussate in the brainstem specifically in the medulla oblongataThe medial lemniscus is formed by the crossings of the internal arcuate fibersThe internal arcuate fibers are composed of axons of nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus.
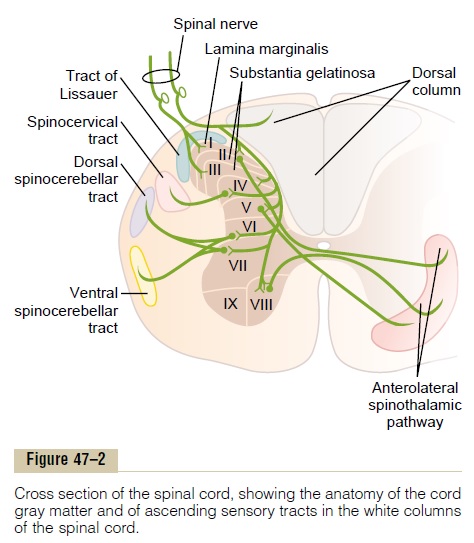
Conscious proprioception most clinically relevant Sensation of. D proprioception and temperature. As well as tactile pressure barognosis graphesthesia stereognosis recognition of texture kinesthesia and two-point discrimination.
It is typically depicted as a chain of three neurons. The DCML system transmits mechanoreceptive sensations from the limbs trunk and posterior part of the head to the dorsal column nuclei in the medulla.
The dorsal-column medial-lemniscus system is particularly responsive to.
It conveys sensation of fine touch vibration pressure two-point discrimination and proprioception position from the skin and joints. The medial lemniscus also known as Reils band or Reils ribbon is a large ascending bundle of heavily myelinated axons that decussate in the brainstem specifically in the medulla oblongataThe medial lemniscus is formed by the crossings of the internal arcuate fibersThe internal arcuate fibers are composed of axons of nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus. Dorsal column - Medial lemniscus DCML pathway. It is typically depicted as a chain of three neurons. The dorsal columnmedial lemniscus pathway is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch vibration two-point discrimination and proprioception from the skin and joints. Medial lemnisci in the brain through the medulla pons mid-brain and to the thalamus. Asked Apr 17 2016 in Psychology by Yarrabean. Medial lemniscus pathway and cuneocerebellar tracts Numerous cutaneous receptors detect and transmit sensory modalities such as light discriminative touch vibration sense proprioception and two-point discrimination. An analogous trigeminal nerve pathway the trigeminal lemniscus serving the face transmits sensory information to the.
Conscious proprioception most clinically relevant Sensation of. The dorsal columnmedial lemniscus pathway is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch vibration two-point discrimination and proprioception from the skin and joints. Medial lemniscus pathway and cuneocerebellar tracts Numerous cutaneous receptors detect and transmit sensory modalities such as light discriminative touch vibration sense proprioception and two-point discrimination. DORSAL COLUMN MEDIAL LEMNISCUS PATHWAY. As well as tactile pressure barognosis graphesthesia stereognosis recognition of texture kinesthesia and two-point discrimination. In the brainstem it is transmitted through the medial lemniscus. The dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway DCML is the sensory pathway responsible for transmitting fine touch vibration and conscious proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebral cortex.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13929/ctAIVoaDrYw1Z2AKQM0afg_Medial_lemniscus_.png)




























Post a Comment for "The Dorsal-column Medial-lemniscus System Is Particularly Responsive To"